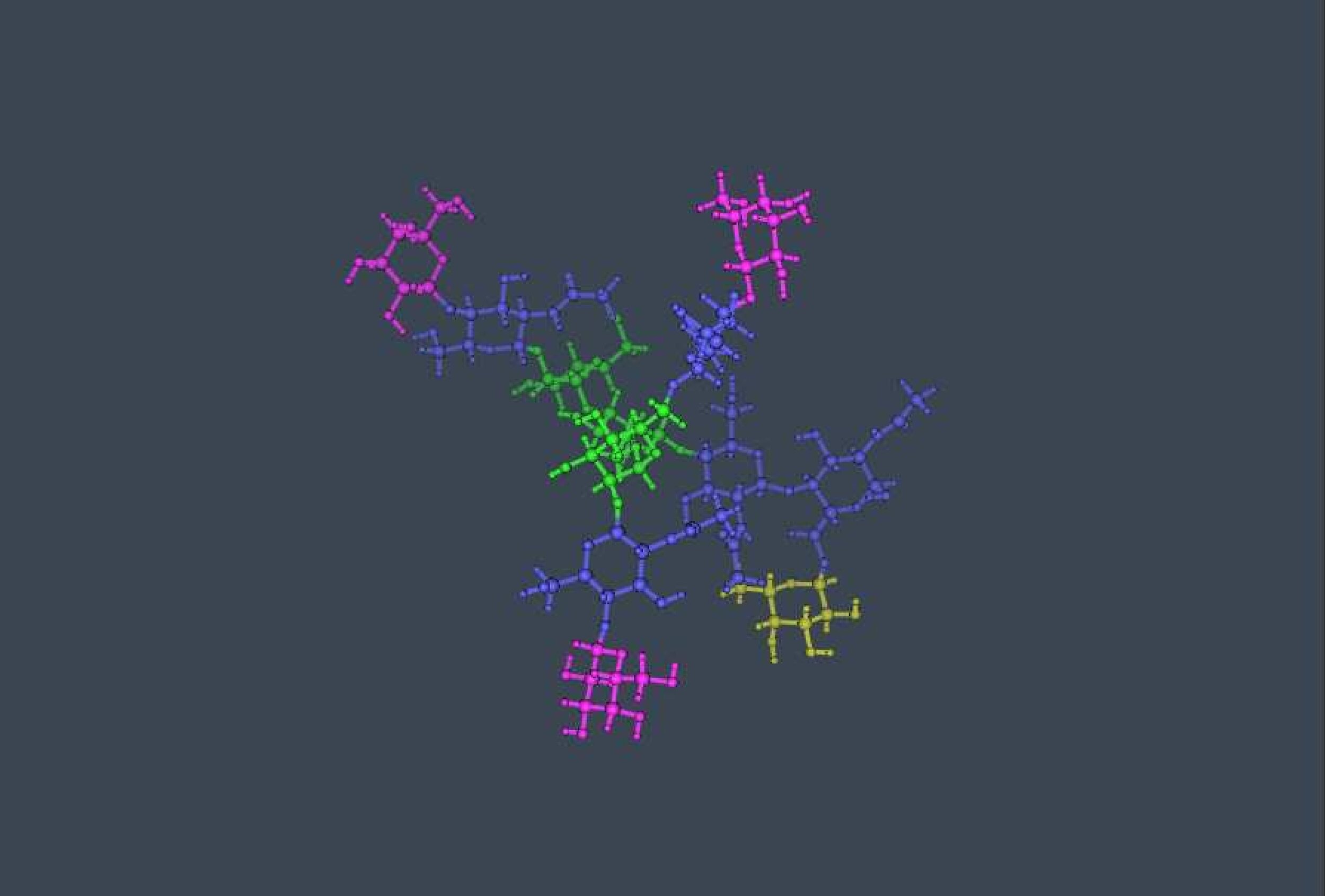
Protein’s Glycosylation
Glycomics #35 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #36 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #37 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics $38 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #39 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #40 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #41 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #42 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #43 (EPO glycosylation)
Glycomics #50_IgG antibody glycosylation 1
Glycomics #51_IgG antibody glycosylation 2
Glycomics #52_IgG antibody glycosylation 3
Glycomics #53_IgG antibody glycosylation 4